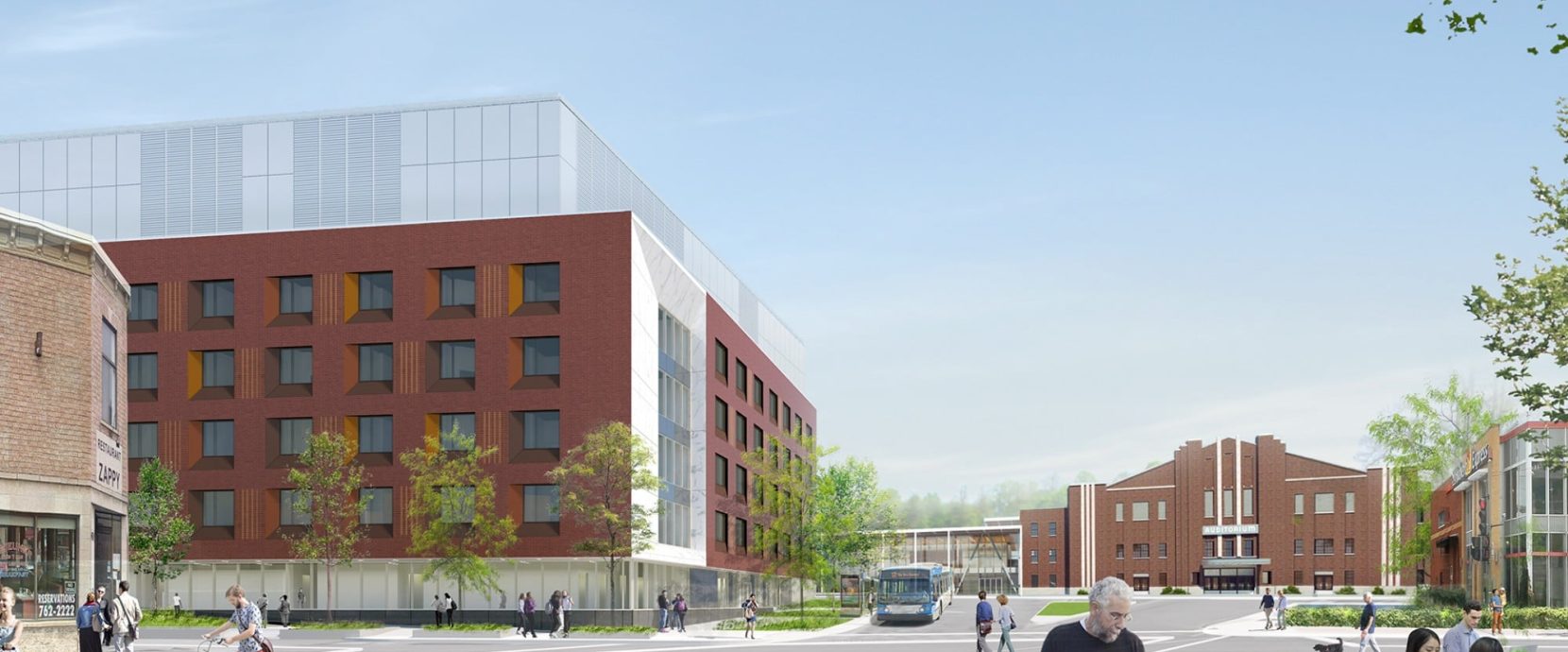
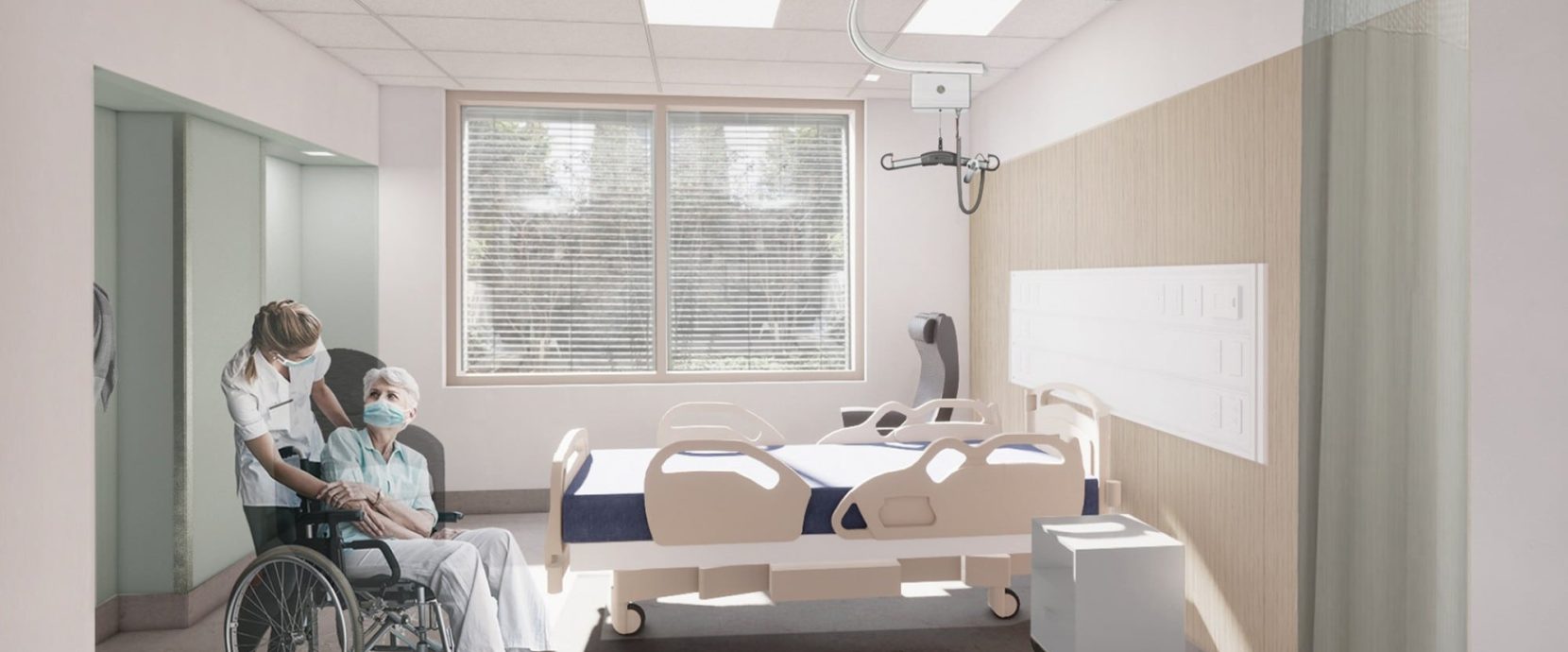
The Verdun Hospital was founded in 1932 and is located in an emerging sector. Over the years, this public establishment has become a reference in the medical field. In a consortium with Norda Stelo, ELEMA was commissioned for the expansion and modernization project of the Verdun Hospital in order to expand and modernize its facilities to better meet the needs of the growing and aging population of its territory. The new construction project will undoubtedly increase the notoriety of this venerable hospital even more.
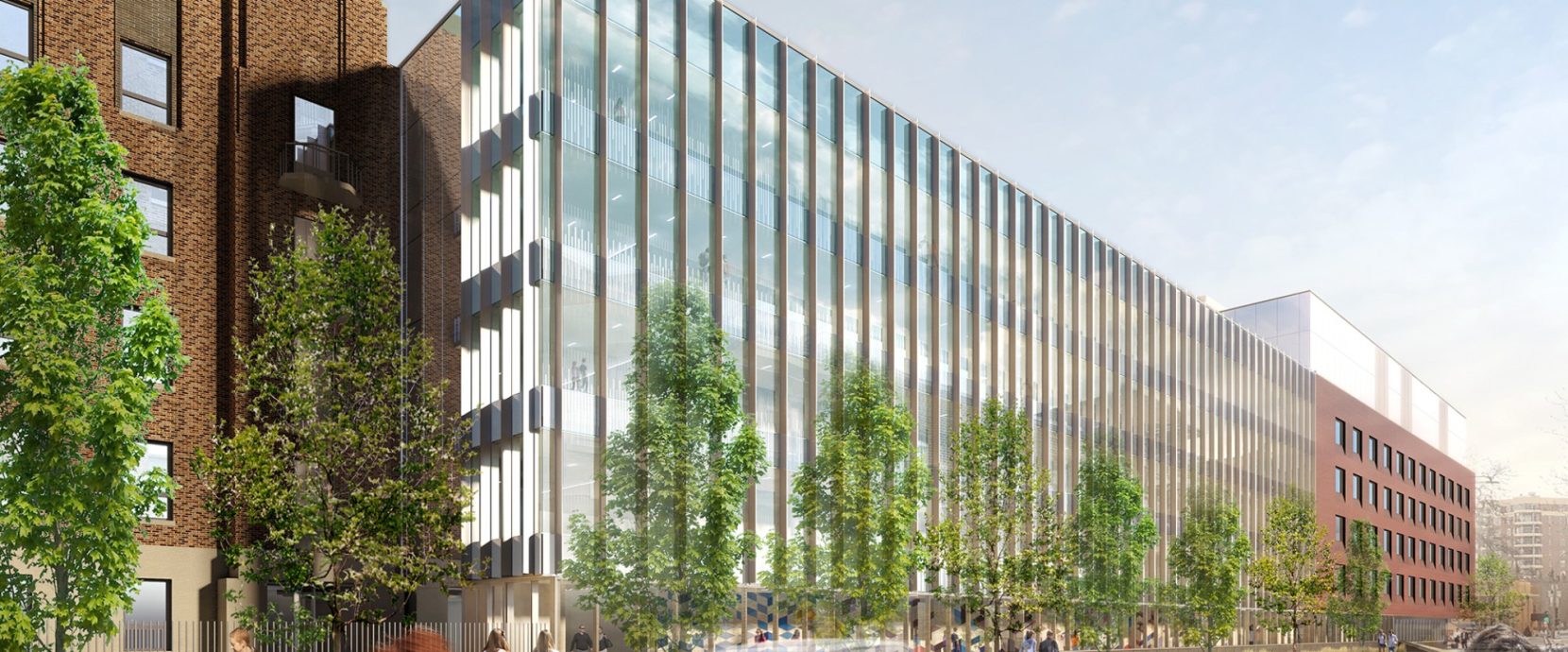
This project will increase the total area of the Verdun Hospital by nearly 50% by adding a new pavilion, a pedestrian bridge connecting the existing building to the new, a redesigned delivery dock and finally by the reconversion of the inner courtyards into an atrium.
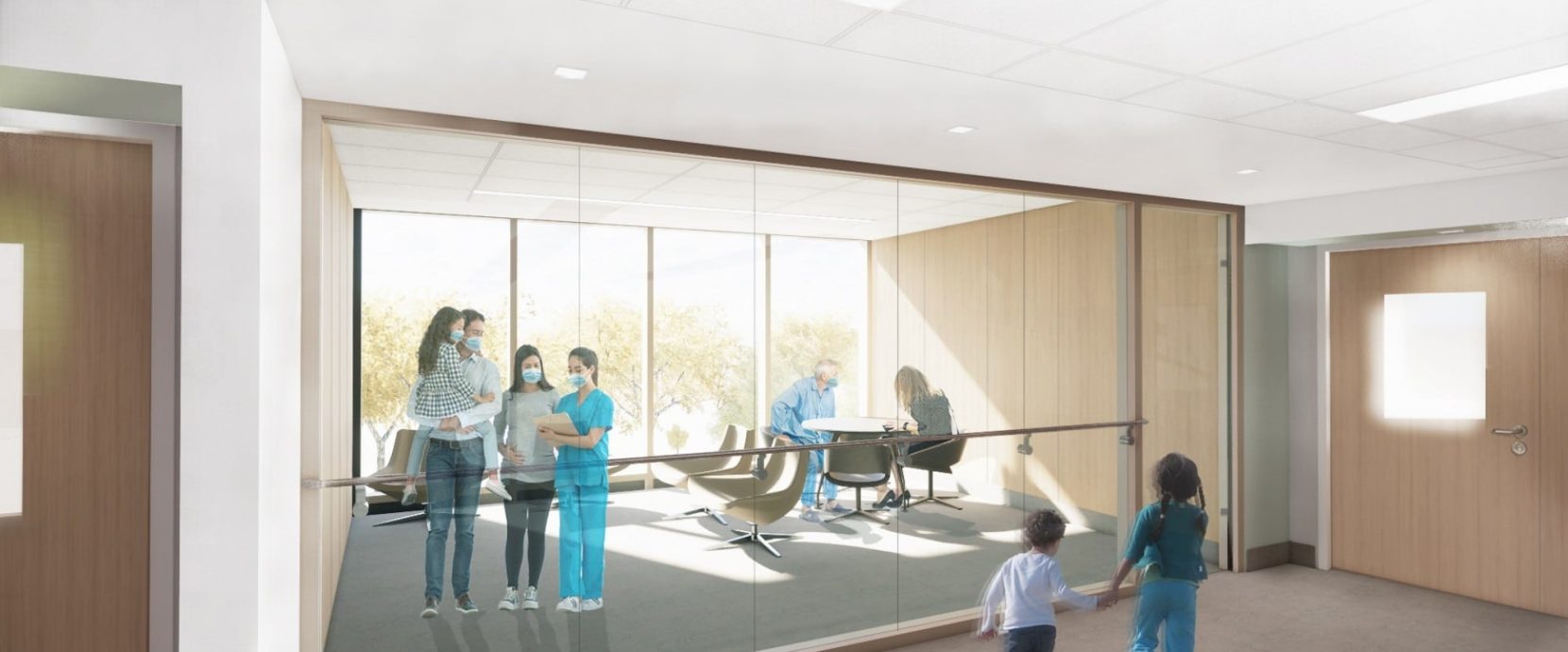
The pedestrian bridge will not only act as a physical link between the old and the new, but also as an architectural facade animated by its pedestrian circulation. It measures 5 storeys in height and has an approximate length of 73 m (240 ft).
The first issue identified in the project was the concern for transparency of the architectural facades, which led to the choice of structural frames resistant to moment. In a second step, the new bridge was to be structurally separated from the existing building in order to avoid a seismic retrofit of the existing pavilions, in accordance with the requirements of the Quebec Building Code.
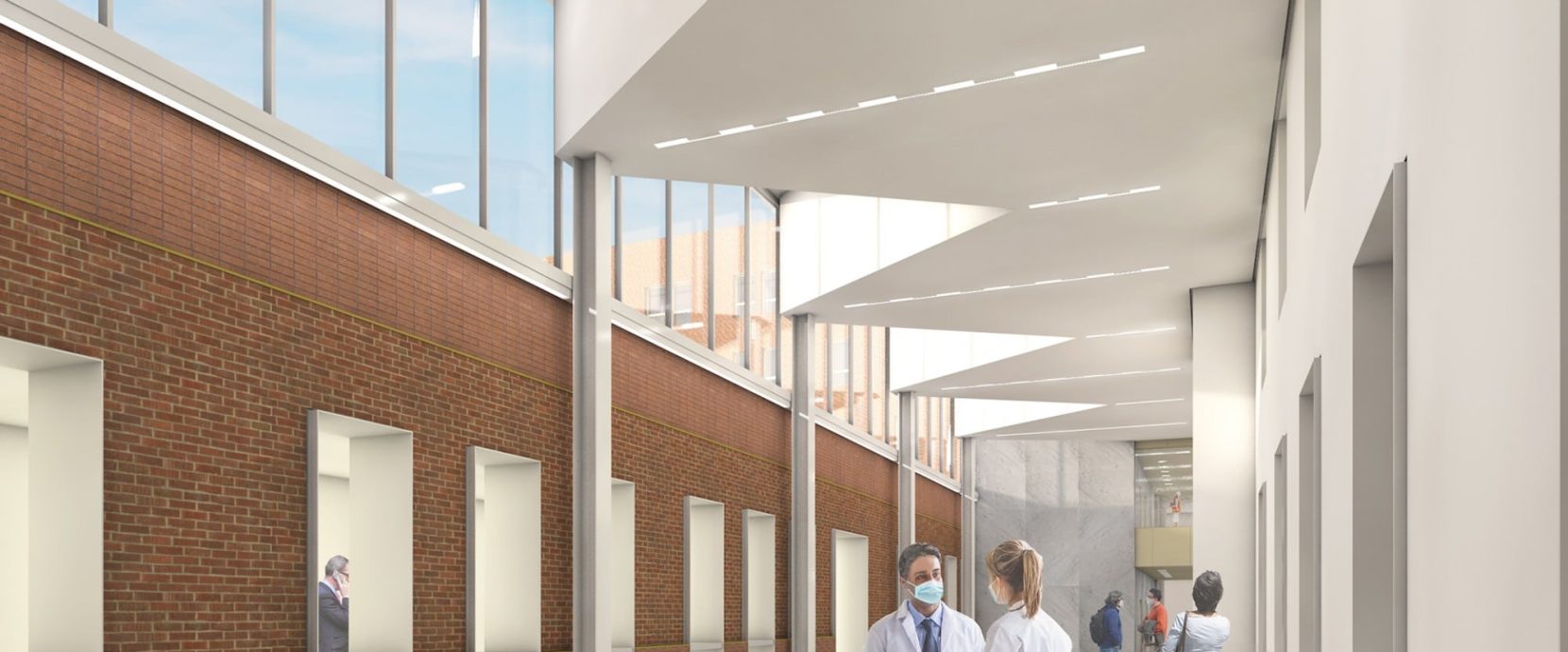
The role of the atrium is to create a new environment by redefining an exterior space that is currently poorly used. An elevator core connecting the new atrium to the existing floors will be added.
* Consortium project